Cannabis Testing
Rose City Labs started with medical marijuana and has been providing cannabis compliance and R&D tests for 10 years.
We make all the OLCC compliance tests for hemp, marijuana and adult use cannabinoids (Potency, Pesticides, Water Activity, Moisture Content, and Residual Solvents) available to all of Oregon. We provide informational tests (such as Mycotoxin, Terpenes, Heavy Metals, and Microbiology) and genetic testing for your marijuana and hemp plants. You can schedule an ORELAP accredited hemp field sampling, cannabis batch sampling, or just provide us with R&D samples for your grow or breeding program. We even offer DIY send-in kits for cannabis virus testing. Our qPCR testing can identify pathogens that can damage hemp and marijuana crops. We’ll help you find what fits your needs!
Compliance Testing
-
Current marijuana testing standards include: pesticides, water activity, moisture content and adult use cannabinoid and CBD concentration. Per recent amendments to OLCC testing, marijuana testing will include mycotoxins beginning July 1, 2022, and heavy metals and microbiological screening starting March 1, 2023.
-
Current testing standards for concentrates and extracts include: pesticides, solvents, and adult use cannabinoid and CBD concentration. Concentrates and extracts will also be subject to the changes to OLCC testing requirements and will have to be tested for: mycotoxins ( July 1, 2022), heavy metals, and microbiological screening (March 1, 2023).
-
Finished inhalable cannabinoid products is a new category of marijuana items under the testing rules. Rules specific to testing them can be found under OAR 333-007-0341. Examples of items that fit under this category are things like infused pre-rolls or inhalable cannabinoid products with non-cannabis additives. These items will be required to be compliance tested once they are finished, but before they are packaged, for pesticides, solvents (if required), adult use cannabinoids and CBD concentration, mycotoxins if manufactured on or after July 1, 2022, heavy metals contaminants if manufactured on or after March 1, 2023, and microbiological contaminants if manufactured on or after March 1, 2023.
-
Hemp field sampling protocols following ODA guidelines and includes 4 hours on-site
-
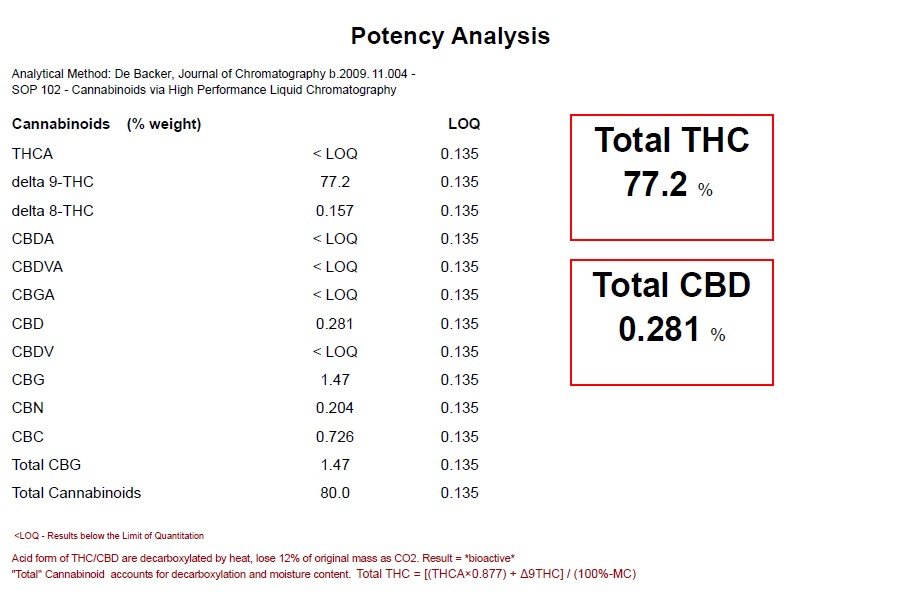
A marijuana item or industrial hemp-derived vapor item must be tested for adult use cannabinoid concentrations. In order to be compliant you will have to test for: delta-9 THC, delta-9 THCA, CBD and CBDA; delta-8 THC testing will be required after July 1, 2022,
Rose City Labs can provide compliance testing and packaging. We also provide cannabinoid analysis for R&D purposes. We test for: delta-9 THC, delta-8THC, THC-A, CBD, CBD-A, CBC, CBG, CBG-A & CBN
-
The use of pesticides in crop cultivation is not new, and cannabis crops are no exception. A pesticide is a substance used for destroying insects or other organisms harmful to cultivated plants or to animals. This can include herbicides for destroying weeds, insecticides for controlling insects, fungicides to prevent mold and mildew, disinfectants to prevent the spread of bacteria, and poisons used to control mice and rats. The most common pesticide classes associated with cannabis are insecticides, acaricides (tick and mite), and fungicides. The OLCC requires pesticide testing for marijuana, concentrates or extracts, industrial hemp-derived vapor items, & finished inhalable cannabinoid products. We test for the 59 pesticides required by the OLCC:
Abamectin, Acephate, Acequinocyl, Acetamiprid, Aldicarb, Azoxystrobin, Bifenazate, Bifenthrin, Boscalid, Carbaryl, Carbofuran, Chlorantraniliprole, Chlorfenapyr, Chlorpyrifos, Clofentezine, Cyfluthrin, Cypermethrin, Daminozide, DDVP (Dichlorvos), Diazinon, Dimethoate, Ethoprophos, Etofenprox, Etoxazole, Fenoxycarb, Fenpyroximate, Fipronil, Flonicamid, Fludioxonil, Hexythiazox, Imazalil, Imidacloprid, Kresoxim-methyl, Malathion, Metalaxyl, Methiocarb, Methomyl, Methyl parathion, MGK-264, Myclobutanil, Naled, Oxamyl, Paclobutrazol, Permethrins, Phosmet, Piperonyl_butoxide, Prallethrin, Propiconazole, Propoxur, Pyrethrins, Pyridaben, Spinosad, Spiromesifen, Spirotetramat, Spiroxamine, Tebuconazole, Thiacloprid, Thiamethoxam, Trifloxystrobin
-
Though the main solvents used in cannabis extraction are butane and ethanol, the OLCC requires solvent testing for cannabis concentrates or extracts, industrial hemp-derived vapor items, & finished inhalable cannabinoid products. Excess butane or ethanol could pose health risks, and other solvents may end up in your cannabis products because they are contaminants of the solvents used in extraction, or because they are used to clean production equipment used in the process. Rose City Labs has been servicing the cannabis industry for a decade and continues to provide testing that meets current and proposed standards, we test for 24 solvents as required by the OLCC.
1,4-Dioxane, 2-Butanol, 2-Ethoxyethanol, 2-Propanol (IPA), Acetone , Acetonitrile, Benzene, Butanes, Cumene, Cyclohexane, Dichloromethane, Ethyl acetate, Ethyl ether, Ethylene glycol, Ethylene Oxide, Heptane, Hexanes, Isopropyl acetate, Methanol, Pentanes, Propane, Tetrahydrofuran, Toluene, Xylenes
-
Aflatoxin B1, B2, G1, G2 and Ochratoxin A
Changes to OLCC testing will require mycotoxins testing as of July 1, 2022.
Aflatoxins are produced by different species of Aspergillus, particularly A.flavus, A.oryzae, A.fumigatus and A.parasiticus. Aflatoxins B1 , B2 , G1 and G2 are particularly dangerous to humans and animals. Aflatoxins are some of the most carcinogenic substances in the environment. They cause liver cancer, and have been linked to other types of cancer. Aflatoxin can lead to liver damage, cancer, mental impairment, abdominal pain, hemorrhaging, coma, and death.
Ochratoxin A (OTA), the most prevalent and relevant fungal toxin produced by Aspergillus species and Penicillium species. Ochratoxin A is formed during the storage of crops and is known to cause a number of toxic effects in animal species. Ochratoxin A is a chronic nephrotoxin, affecting kidney function. In addition to being a nephrotoxin, animal studies indicate that ochratoxin A is a liver toxin, an immune suppressant, a potent teratogen, and a carcinogen. OTA is suspected of being the main agent responsible for human Balkan endemic nephropathy (BEN) and associated urinary tract tumors.
-
Marijuana, concentrates or extracts, industrial hemp-derived vapor items, & finished inhalable cannabinoid products will be tested for arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury as part of heavy metals testing requirements beginning March 1st, 2023.
Cannabis plants have traits that facilitate the absorption of heavy metals including: long stem length, fast growth, high root and leaf surface area, high photosynthetic activity and dependence on relatively few nutrients for survival. Heavy Metals like lead, cadmium and chromium, can be transported and distributed through the stalk, into the leaves and flowers of marijuana plants. These heavy metals then exit the plant through trichomes.
-
Microbiological contaminants will need to be tested in accordance with OAR 333-007-0390 starting March 1, 2023. Batches will be tested for:
Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC), Salmonella, and Aspergillus; A. flavus, A. fumigatus, A. niger, A. terreus.
Cannabis Genetics/R&D Testing
-
Rose City Labs Uses Medicinal Genomics’ PathoSEEK® Microbial testing safety platform to test for mold, mildew, bacteria, and hemp mites.
-
The FemINDICAtor® qPCR Plant Gender Detection Assay uses DNA technology to identify male cannabis plants weeks before they show any visual sex features. Males can then be removed from a grow in order to maintain female flowers rich in cannabinoids. This method is an improvement over traditional visual inspection because it allows growers to identify male plants earlier, more accurately, and with less labor.
-
Plant genetics can be coached to express varying concentrations of cannabinoids, but the relative ratios of the key cannabinoids, THCA and CBDA, are usually genetically determined. As an example, there are no known agricultural methods to make a CBDA-dominant strain become a THCA-dominant strain via environmental conditions. These critical chemotypes are governed by gene knock outs in their respective enzymatic synthases (CDBA Synthase and THCA Synthase).
-
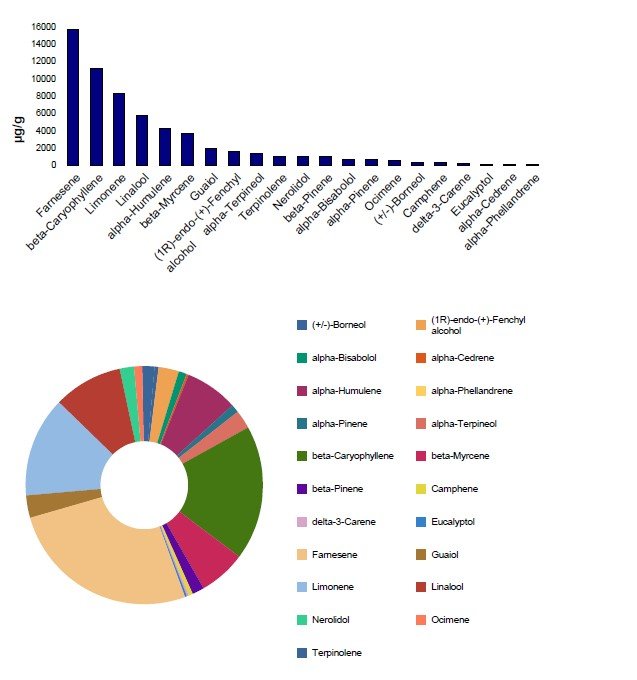
A lot of attention is given to THC potency and cannabinoid concentrations, but cannabis connoisseurs are increasingly looking at terpene profile as the true measure of quality extracts and concentrates. Each cannabis strain has its own profile. Our terpene test results will provide you with a readout of your samples’ terpene profile.
Terpenes are valued for their flavor and therapeutic effects. Terpenes are naturally occurring chemical compounds found in plants and some animals. Though cannabis contains a variety of terpenes in high concentrations, most people are familiar with terpenes from spices, teas, and essential oils we use every day. The fragrance of most plants is due to a combination of terpenes, which create the characteristic scent of plants like pepper, pine, lavender, and cannabis. We test for 42 Terpenes:
n-Nonane, a-Pinene, Camphene, Sabinene, ß-Myrcene, ß-Pinene, a-Phellandrene, Carene, a-Terpinene, ß-Ocimene, Limonene, trans-ß-Ocimene, Eucalyptol, g-Terpinene, Terpinolene, Sabinene Hydrate, Linalool, (+/-)-Fenchone, (+)-Fenchyl alcohol, Isopulegol, (+/-)-Camphor, Isoborneol, Menthol, (+/-)-Borneol, a-Terpineol, g-Terpineol, Nerol, Geraniol, (+)-Pulegone, Geranyl acetate, cis-Farnesene, trans-Farnesene, a-Cedrene, beta-Caryophyllene, a-Humulene, Valencene, cis-Nerolidol, trans-Nerolidol, Guaiol, Caryophyllene oxide, (+)-Cedrol, a-Bisabolol
Our reports include detailed information about your sample.
Genomic tools save time and deliver important insights.
Here’s what you can do with the data…
Screen for known variants
Identify marijuana plants with desirable traits, such as cannabinoid and terpene synthase, pathogen resistance, sex determination, and more!
Find novel variants
Identify plants with amino acid changing variants that could affect cannabinoid production.
Build an IP Case
Use genetic information about your cultivar to prove prior art or demonstrate novelty.
Stabilize genetics
Monitor heterozygosity values to stabilize genetics and reduce variability among progeny.
Determine Rarity
Find out how rare your cultivar is or identify potential breeding partners when you compare it to other cultivars in the Kannapeida database.
Verify Genetics
Compare your plant’s specific DNA code to known marijuana cultivars and determine whether you are growing or selling your desired strain.